THEORY
For determining the grain size distribution of soil sample, usually
mechanical analysis (sieve analysis) is carried out in which the finer sieve used is 75 micron or the nearer opening.
If soil contains appreciable quantities of fine fractions in (less than 75 microns) sedimentation analysis
is done. The two methods of sedimentation analysis are Hydrometer method and Pipette method.
Hydrometer method is more convenient, while pipette method is more accurate.
APPARATUS
Hydrometer, Glass measuring cylinder-Two of 1000 ml capacity with ground
glass or rubber stoppers about 7cm diameter and 33 cm high marked at 1000 ml volume, Thermometer- To cover the
range 0 to 50°C with an accuracy of 0.5°C, Water bath, Stirring apparatus
, I.S sieves apparatus, Balance accurate to 0.01 gm, Oven-105 to 110, Stop
watch, Desiccators
Porcelain evaporating dish, Wide mouth conical flask, or conical beaker of 1000 ml capacity, Thick funnel-about 10 cm in diameter, Filter flask-to take the funnel, Measuring cylinder-100 ml capacity, Wash bottle-containing distilled water, Filter papers, Glass rod-about 15 to 20 cm long and 4 to 5 mm in diameter, Hydrogen peroxide-20 volume solution, Hydrochloric acid N solution-89 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid.(specific gravity 1.18) diluted with distilled water one litre of solution, Sodium hexametaphosphate solution-dissolve 33 g of sodium hexametaphosphate and 7 gms of sodium carbonate in distilled water to make one liter of solution.
CALIBRATION OF HYDROMETER
Volume
(a) Volume of water displaced:
Approximately 800 ml of water shall be poured in the 1000 ml measuring cylinder. The reading of the water level shall be observed and recorded.
The hydrometer shall be immersed in the water and the level shall again be
observed and recorded as the volume of the hydrometer bulb in ml plus volume of that part of the stem
that is submerged. For practical purposes, the error in the inclusion of this stem volume may be
neglected.
(b) From the weight of the hydrometer: The hydrometer shall be weighed to the
nearest 0.1 gm. The weight in gm shall be recorded as the volume of the bulb plus the volume of
the stem below the 1000ml graduation mark. For practical purposes, the error due to the inclusion
of this stem may be neglected.
Calibration
(a ) The sectional area of the 1000 ml measuring cylinder in which the
hydrometer is to used shall be determined by measuring the distance between the graduations. The sectional
area is equal to the volume include between the two graduations divided by the measured distance
between them.
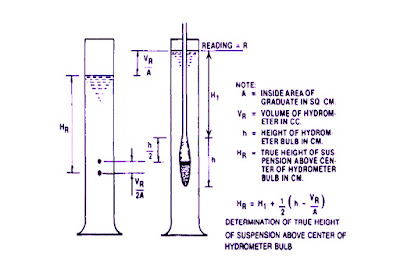
Place the hydrometer on the paper and sketch it. On the sketch note the lowest and highest readings which are on the hydrometer and also mark the neck of the bulb. Mark the center of the bulb which is half of the distance between neck of the bulb and tip of the bulb.
(b) The distance from the lowest reading to the center of the bulb is (Rh) shall be recorded (Rh =HL + L/2).
(c) The distance from the highest hydrometer reading to the center of the bulb
shall be measured and recorded.
(d) Draw a graph hydrometer readings vs HH and RH. A straight line is obtained. This calibration curve is used to calibrate the hydrometer readings which are taken with in 2 minutes.
(e) From 4 minutes onwards the readings are to be taken by immersing the hydrometer
each time. This makes the soil solution to rise, there by rising distance of free fall of the
particle. So correction is applied to the hydrometer readings.
(f) Correction applied to the Rh and HH
Vh= Volume of hydrometer bulb in ml.
A=Area of measuring cylinder in cm2.
From these two corrected readings draw graph (straight line)
Calculation
Date:
Sample No:
Total weight of dry soil taken, W =
Specific Gravity of soil, G =
Hydrometer No._____________ Wt. Of soil gone into solution ,Ws =
Meniscus correction, Cn =Dispersion agent correction =
Reading in water RW =
Temperature correction =
% finer for wt. Of soil Ws gone into solution N= [(100G)/ {Ws x (G)}] x R
|
Date |
Time |
Elapsed |
Hydrometer |
Corrected |
Zr |
Velocity |
Equivalent |
R |
N |
REMARKS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Physical properties of minerals
- Determination of natural moisture of soil
- Determination of specific gravity of soil
- Sand replacement method
- Sieve analysis-Grain distribution
- Hydrometer analysis of soil
- Determination of liquid limit
- Determination of Plastic limit
- Determination of Shrinkage limit
- Direct shear test
- Proctor test
No comments:
Post a Comment